If you live with diabetes, you probably know that it is important to achieve good hemoglobin A1c (or HBA1C for short) levels.
But what exactly is HBA1C? What is the “regular” HBA1C level? How can you achieve and maintain that?
In this article, we will dig deep into the numbers and explain the constantly ejected HBA1C.
What is the HBA1C test?
HBA1C is a blood test that communicates the average blood glucose level for the past 2-3 months. HBA1C stands for “glycation haemoglobin test” or glycohemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells, giving the blood a red colour, and its job is to carry oxygen throughout the body.
In particular, HBA1C tests measure the average amount of blood glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells over the past few months.
Red blood cells only live for about three months before they regenerate. This is why the test shows average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months.
How often should I test HBA1C?
Diabetic patients are advised to get tested between 2-4 times a year (if the patient is pregnant or has a change in insulin therapy).
However, there are some modernity biases in the test, and if blood glucose levels are high for the weeks before taking the test, your HBA1C counts will also be higher.
It is also important to note that the HBA1C test is the average of all blood glucose levels over the past few months, averaging all highs and all drops. This can give you a distorted feeling about what your blood sugar control actually is.
How does the HBA1C test work?
HBA1C tests are usually conducted in the lab and can be done via a traditional blood draw (intravenous) or finger stick (instant results).
If you are taking blood via a draw of blood from the vein, the results may take several days to return.
The test takes less than 5 minutes to complete. Unlike fasting glucose tests, there is no need to fast before taking the test and you can do it anytime.
You can also run your tests yourself using a simple and reliable home test kit.
This video shows how easy it is for Christel Oerum to measure A1C at home.
What is “regular” HBA1c?
This depends on the person, but roughly speaking, the HBA1C results are given as percentages.
- Normal, non-diabetic: HBA1C under 5.7%
- Prediabetes: HBA1C from 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes (does not decipher type): HBA1C over 6.5%
However, if you have gestational diabetes or existing diabetes, you should work with your doctor to understand your individual health goals, taking into account your lifestyle, stage of life and what’s long-term sustainable.
Women who become pregnant after suffering from existing diabetes have stricter HBA1C goals, for example, during pregnancy. This number should normally be less than 6%.
Elderly people, and those who cannot easily feel hypoglycemia (also known as “hypoare”), may need to have a higher HBA1C goal to prevent dangerous hypoglycemia (hypoglycemia).
Athletes can also choose higher HBA1C levels to facilitate training and maintain stamina, but newly diagnosed people with diabetes can aim for HBA1Cs of mid-time from 5S as they are experiencing the “honeymoon stage” of intermittent insulin production from the pancreas.
However, if you live with diabetes (any type) without lifestyle-specific goals, the American Diabetes Association recommends keeping your HBA1C levels below 7%.
Talk to your doctor to ensure you have established individual goals to work for you and your life. There is no “regular” HBA1C percentage that everyone should aim for.
Related: How to convert A1c to blood sugar levels
Why is the HBA1C test important?
HBA1C is most important in the diagnosis of diabetes, pre-diabetes, and even gestational diabetes (although glucose tolerance testing is more efficient and beneficial).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults age 45 and older take the HBA1C test to screen for diabetes and diabetes. If results are normal, the provider will recommend schedule retests based on your age and risk factors.
If your results indicate prediabetics, you should take repeated tests every 1-2 years. If you have prediabetics, you should consult your doctor about the steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
If you are under the age of 45 but exhibit certain risk factors, your doctor may recommend the HBA1C test, which includes:
- Being overweight or obese
- I have high blood pressure (high blood pressure)
- I have heart disease
- Sedentary lifestyle/physical inactivity
Regardless of your age, it is a sign of diabetes, so if you experience the following symptoms, you should call your doctor immediately:
- Extreme thirst
- Weight loss
- Haze
- Despite losing weight, extreme hunger
- Fruity scented breath
- Extreme fatigue
- Body pain
- headache
- confusion
Your doctor may recommend getting an HBA1C test or seeking emergency medical care, depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Existing diabetes patientsdetermine using the HBA1C test General Controlling diabetes over the past few months.
It may serve as a guide to picking up problems you may be experiencing with both hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic levels, improving your health and preventing diabetic complications such as heart disease, retinopathy, kidney disease, hypertension, amputation, blindness, and early death.
Studies have shown that even a 1% reduction in HBA1C reduces the likelihood of developing retinopathy by 37%!
Disadvantages of the HBA1C test
Standard HBA1C tests have undergone some scrutiny recently due to the fact that they are merely a small portion of average blood glucose and hypoglycemia levels.
As more and more diabetics adopt continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology for diabetes, the widespread adoption of range of glycemic control (TIR) measures, which leads to an increasing number of existing diabetic patients.
Time within range measures the percentage of days when blood sugar levels fall within a certain range (usually 70 mg/dl-180 mg/dl).
In this case, the higher the percentage is better, as this means your blood sugar levels will swing less and are within the target range for most of the day.
Researchers believe this is actually a better measure of overall control, as they can accurately identify where and when blood sugar levels are spiked or dropped, and can see how much they are in a healthy range of blood sugar levels.
Because HBA1c is merely average, it cannot provide the same detailed data, which can be misleading. If you have a lot of high blood sugar of 400 mg/dL and a low nighttime of 60 mg/dL, HBA1C can incorrectly give you a “healthy” percentage.
The graph below shows how three people can have the same average blood glucose level, but the range is very different.
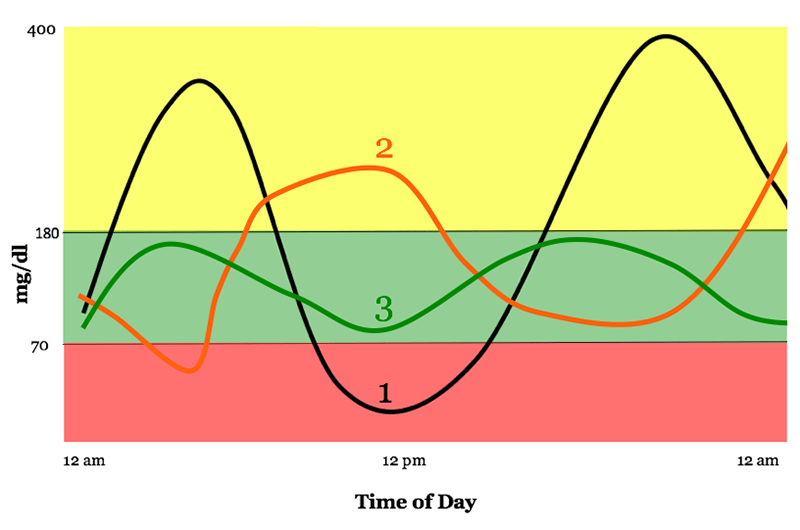
For the time being, most providers rely on both TIR and HBA1C to provide the best possible picture of patient glucose management and control.
And of course, for those who have no access to CGM technology, time within range is impossible and they need to rely on traditional HBA1C tests.
Read our comprehensive guide to find out more about HBA1C and how to manage it. How to lower A1c.